Webb House Telescope detects quartz crystals in WASP-17 b exoplanet’s environment

[ad_1]
In context: WASP-17 b is a “sizzling Jupiter” sort exoplanet that orbits a number star situated 1,300 mild years away from Earth. This gasoline big is among the three targets within the JWST-powered “Deep Reconnaissance of Exoplanet Atmospheres utilizing Multi-instrument Spectroscopy” (DREAMS) investigations, and it has already furnished researchers with surprising information.
WASP-17 b’s environment is extremely harsh and consists of aerosols, that are tiny silicon dioxide particles, generally referred to as silicate. Silicate is a mineral plentiful in silicon and oxygen, ceaselessly discovered on Earth and different rocky objects within the type of quartz. Silicate grains recognized within the atmospheres of exoplanets and brown dwarf stars up to now had been sometimes wealthy in magnesium, not quartz. Nonetheless, WASP-17 b has confirmed to be an exception.
A workforce of scientists from NASA and the College of Bristol employed the Mid-Infrared Instrument (MIRI) on the James Webb Telescope to look at this huge planet. They initially anticipated to seek out magnesium silicates suspended within the planet’s dense environment however had been shocked to discover pure quartz particles (SiO2) as an alternative. With a quantity over seven instances that of Jupiter and half the mass, WASP-17 b ranks among the many largest exoplanets ever discovered.
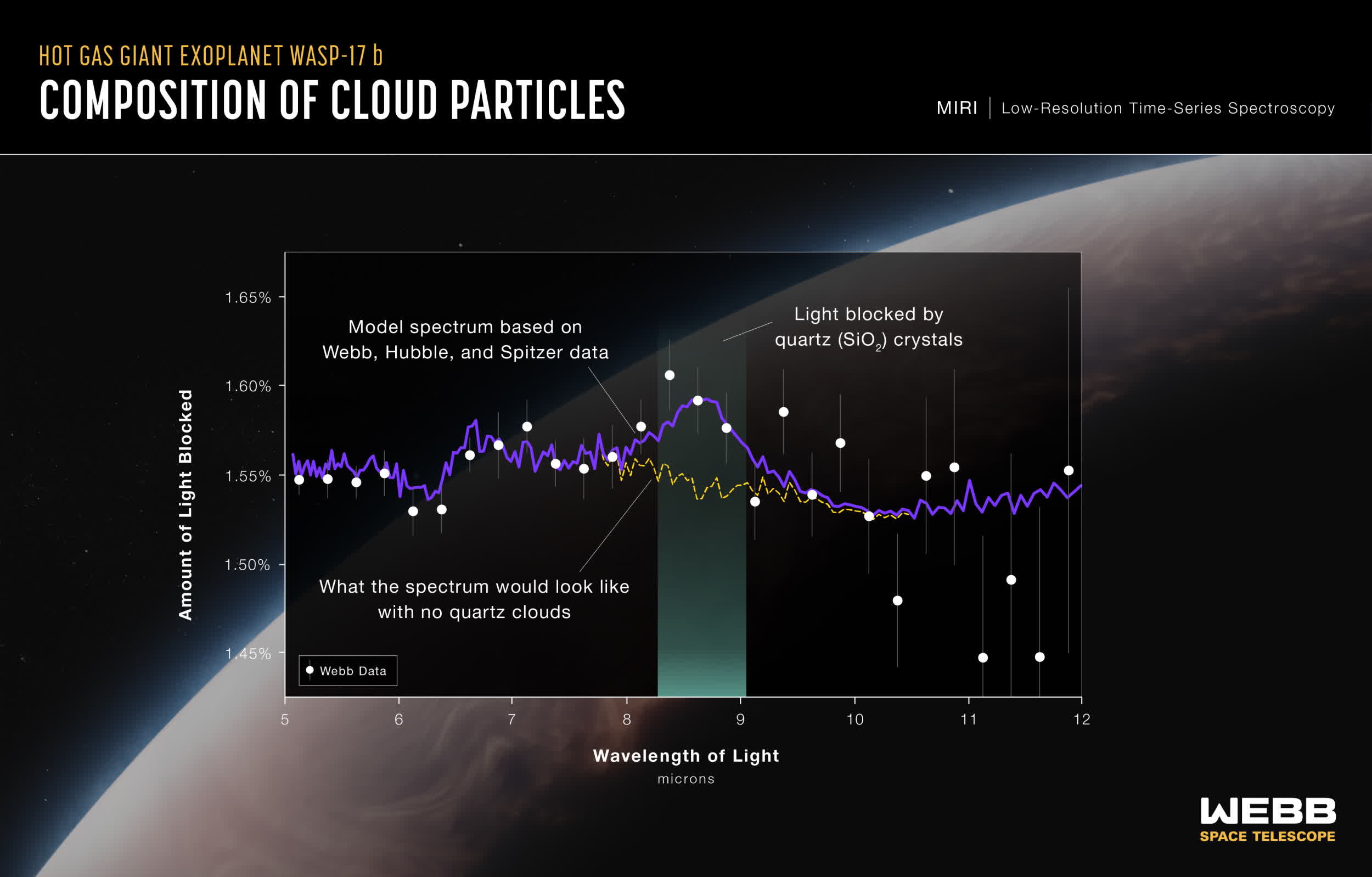
The workforce carried out observations of the planet for almost 10 hours, acquiring over 1,275 “brightness measurements” inside the infrared vary of the electromagnetic spectrum, particularly between 5 and 12 microns. The researchers employed a method known as “transmission spectroscopy,” which entails measuring the affect of a planet’s environment because it passes in entrance of its host star.
JWST devices detected a definite “bump” at 8.6 microns, which the scientists clarify is a transparent indicator of quartz being current within the clouds enveloping WASP-17 b. Moreover, through the use of observations in seen and near-infrared mild collected with the venerable Hubble House Telescope, the workforce managed to calculate the scale of the aerosol crystals, which turned out to be roughly 10 nanometers in diameter.
The invention of oxygen-rich silicates in WASP-17 b’s environment holds important significance, because the scientists emphasize. They level out that if we solely account for the oxygen in gaseous kind and neglect the oxygen saved inside minerals like quartz (SiO2), we might considerably underestimate the whole oxygen abundance in a planet’s surroundings.
WASP-17 b is among the three exoplanets chosen for the DREAMS investigation plan, which is designed to gather a “complete” vary of observations involving varied forms of celestial objects. The plan’s targets embody a “sizzling Jupiter” (WASP-17 b), a “heat Neptune,” and a temperate rocky planet.
[ad_2]
Source