Nvidia G-Sync vs AMD FreeSync in 2023 and 2024

[ad_1]
Have you ever ever been researching your subsequent monitor buy, solely to run into phrases like G-Sync, FreeSync, adaptive sync, and VRR – with out absolutely understanding what they imply, or how they differ? Do you wish to understand how G-Sync compares to FreeSync and whether or not your graphics card might be suitable along with your monitor?
On this article, we’ll reply these questions in a means that is related in at present’s monitor market, circa 2023-2024. Now we have coated this matter several times before, but it surely’s been considerably of a transferring goal as applied sciences mature and assist improvs, so this is our full replace.
What’s Adaptive Sync?
Adaptive sync is a vital characteristic constructed into trendy gaming displays. It permits the show refresh rate – what number of instances the monitor can replace the picture on display per second – to synchronize along with your PC’s render price – what number of frames per second your GPU is rendering.
When the refresh price and render price are synchronized, the show’s refresh price will adapt to the output out of your PC and range the refresh price as wanted. For this reason it is known as “adaptive sync” or “variable refresh price (VRR).”
When adaptive sync is enabled and functioning correctly, the refresh price of your show will match the FPS you are getting in your sport. For instance, if a sport runs at 126 FPS on a 144Hz monitor with adaptive sync enabled, the monitor will function at 126 Hz as a substitute of 144Hz. If the sport’s FPS drops to 114, the monitor will scale back its refresh price to 114Hz, adapting to the FPS output and ranging its refresh price.
This synchronization affords a number of advantages whereas gaming. At any time when there is a mismatch between FPS output and refresh price – as an example, operating a sport at 126 FPS on a hard and fast 144Hz monitor – you may encounter a subpar expertise in certainly one of two methods:
- With out Vsync, you may expertise display tearing, the place the show and GPU output replace at totally different charges. When the GPU begins rendering a brand new body whereas the show is mid-refresh cycle, a visual tear happens between the 2 frames, creating an disagreeable visible artifact, significantly when the frames differ considerably.
- With Vsync – which differs from adaptive sync – the GPU delays its freshly rendered body till the following show refresh cycle begins to forestall tearing. Nonetheless, if the show refreshes quicker than the GPU’s output, Vsync causes body duplication on display, resulting in stutter and judder as you alternate between receiving a brand new body on each show replace and seeing a repeated body. Vsync additionally will increase enter latency for the reason that GPU should buffer and maintain every body till the following refresh cycle.
Adaptive sync solves each points. By synchronizing the refresh cycle and render price, it prevents the show from receiving a brand new body mid-refresh, eliminating tearing. Because the refresh price adjusts to match the GPU’s output, the GPU does not must duplicate frames, decreasing judder, and it does not need to delay frames, thus reducing enter lag.
FreeSync and G-Sync monitor compatibility
When discussing the trendy implementation of adaptive sync in displays, graphics playing cards, and software program, FreeSync and G-Sync are basically model names from AMD and Nvidia, respectively.
When adaptive sync was a brand new expertise, there have been important variations between FreeSync and G-Sync. In case you owned an AMD graphics card, solely FreeSync displays had been suitable, and equally, when you had an Nvidia graphics card, solely G-Sync displays would work. Nonetheless, usually at present, that is now not true…
FreeSync and G-Sync displays are suitable with each AMD and Nvidia graphics playing cards. Meaning FreeSync displays work with Nvidia GPUs, and G-Sync displays work with AMD GPUs.
Because it at the moment stands, FreeSync and G-Sync are largely getting used as advertising and marketing instruments, permitting producers to characteristic them on their merchandise and spec sheets. Nvidia encourages house owners of their GPUs to purchase G-Sync displays, and AMD encourages their GPU house owners to go for FreeSync, however basically, that is only a advertising and marketing technique and never a requirement. In case you encounter a FreeSync monitor and are involved about its compatibility along with your Nvidia-powered PC, relaxation assured, it is going to work simply effective.
Nvidia has been supporting FreeSync displays for almost 5 years. Full adaptive sync compatibility is obtainable over DisplayPort on GeForce GTX 10 sequence GPUs or newer, and over each DisplayPort and HDMI on GeForce GTX 16 and RTX 20 sequence GPUs or newer. Which means the overwhelming majority of present Nvidia graphics card house owners can absolutely make the most of FreeSync displays and, by extension, all adaptive sync displays.
The state of affairs is a little more complicated on the AMD aspect. Briefly, AMD GPU house owners can use adaptive sync performance on all G-Sync Appropriate branded displays, in addition to on displays outfitted with a G-Sync module launched since roughly the tip of 2019. It is because Nvidia up to date the G-Sync {hardware} module round late 2019 to assist generic adaptive sync along with Nvidia’s earlier proprietary resolution.
Because of this, early G-Sync displays are solely suitable with Nvidia graphics playing cards, however virtually any monitor launched within the final 4 years works properly with each Nvidia and AMD GPUs, in addition to Intel GPUs and a few gaming consoles.
Nvidia G-Sync branding defined
Transferring on, you should still be questioning what’s G-Sync Appropriate and why a {hardware} G-Sync module is required? Let’s now break down Nvidia’s technique with G-Sync.
Adaptive sync as a expertise have to be carried out in each the monitor and the graphics card to perform correctly. Subsequently, Nvidia has branded their implementation of their graphics playing cards as G-Sync. Initially, this referred to Nvidia’s proprietary resolution: customized expertise built-in into each the GPUs and G-Sync displays.
However at present we’ve got extra generic, industry-standard adaptive sync options with broad compatibility that do not require Nvidia-specific {hardware}. Nonetheless, Nvidia continues to model their implementation of adaptive sync as G-Sync.
There are three courses of G-Sync: G-Sync Appropriate, G-Sync, and G-Sync Final. Fairly complicated, however they every have distinct meanings.
G-Sync Appropriate
| Nvidia G-Sync Appropriate |
| Helps Generic Adaptive Sync |
| Nvidia Licensed & Validated |
| Adaptive Sync Enabled in Driver by Default |
G-Sync Appropriate refers to displays that assist generic adaptive sync and are licensed by Nvidia to work with their merchandise. Nvidia claims they validate these displays to make sure they do not flicker, pulse, or present artifacts throughout gaming and mechanically allow adaptive sync for these merchandise within the driver by default. Nvidia frequently updates their driver whitelist with G-Sync Appropriate merchandise, recurrently including new displays.
Nvidia G-Sync
| Nvidia G-Sync |
| Makes use of Nvidia’s G-Sync {Hardware} Module |
| Fashionable Modules Help Generic & Propietary Adaptive Sync |
| Variable Overdrive Help |
| Extra Validation & Calibration |
| Unique Options on Some Displays (ULMB2, Reflex Analyzer) |
| Module Downsides: Costly, Energy Hungry, No HDMI 2.1 |
G-Sync, with out the “Appropriate” designation, applies to displays incorporating Nvidia’s {hardware} G-Sync module, a show scaler that replaces normal scalers supporting generic adaptive sync. Fashionable G-Sync modules assist each Nvidia’s legacy proprietary adaptive sync resolution and generic adaptive sync.
Displays utilizing the G-Sync module supply sure efficiency advantages, like variable overdrive, sometimes present in G-Sync displays however much less widespread in G-Sync Appropriate or non-G-Sync displays. Nvidia additionally conducts extra intensive tuning on G-Sync displays, together with shade calibration, often producing above-average outcomes. Some G-Sync displays characteristic Nvidia-exclusive options like ULMB2 and the Reflex Analyzer.
Nonetheless, the G-Sync module does have some downsides. It is costly to supply, typically leading to a better value for shows in comparison with comparable fashions utilizing common scalers. It is comparatively power-intensive, rising energy consumption and often requiring energetic cooling through a built-in fan. Moreover, in its present kind, it does not assist some trendy options like HDMI 2.1. Over time, extra monitor producers are selecting G-Sync Appropriate merchandise over G-Sync.
Nvidia G-Sync Final
| Nvidia G-Sync Final |
| Makes use of Nvidia’s G-Sync {Hardware} Module |
| Elevated HDR Help |
| 1,000 Nits Brightness, Multi-Zone Backlight, Large Shade Gamut |
| Highest Resolutions & Refresh Charges |
G-Sync Final refers to displays utilizing the G-Sync module that additionally assist an elevated stage of HDR. Nvidia states these displays supply 1,000 nits of brightness, multi-zone backlights, and vast shade gamut assist, together with excessive resolutions and refresh charges – along with the advantages of displays with the G-Sync module.
Initially, G-Sync Final ensured true HDR assist with full array native dimming LCD backlights or OLED panels. Nonetheless, this normal was relaxed a number of years in the past to incorporate edge-lit panels, making it much less indicative of premium HDR high quality. G-Sync Final displays at the moment are uncommon, with many true HDR merchandise, together with most OLEDs, utilizing common scalers as a substitute of the G-Sync module.
In abstract, G-Sync Appropriate displays are these with generic adaptive sync assist that Nvidia claims to certify and may have adaptive sync enabled by default within the driver. The G-Sync branding represents a better tier utilizing Nvidia’s G-Sync {hardware} module with extra tuning and certification. G-Sync Final is the very best tier, reserved for displays supporting HDR and utilizing the G-Sync module.
The right way to allow G-Sync on Non-G-Sync branded displays
The one actual, constant distinction we have noticed throughout intensive monitor testing between a show branded as G-Sync Appropriate and one with out G-Sync branding is that the latter won’t have adaptive sync enabled by default. That is it.
The absence of G-Sync branding doesn’t indicate that the product is of poor high quality or would fail Nvidia’s certification, nor does it point out incompatibility with Nvidia GPUs. Actually, a number of the best monitors on the market today, such because the Alienware AW3423DWF, aren’t G-Sync Appropriate, but they ship glorious efficiency and work seamlessly on Nvidia GPUs with full adaptive sync assist.
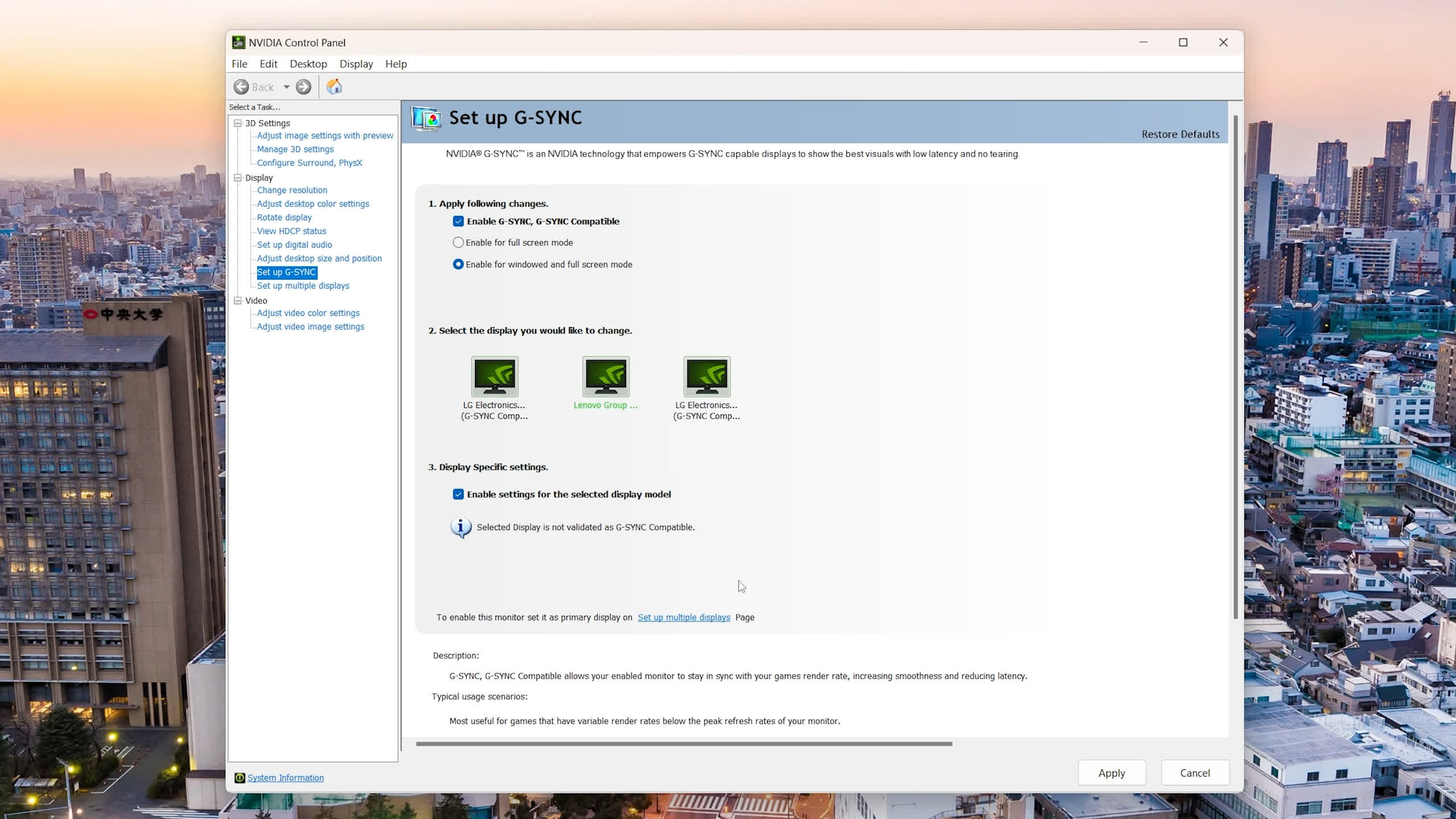
If you are going to buy a monitor not branded as G-Sync or G-Sync Appropriate, to allow adaptive sync on an Nvidia GPU, merely open the Nvidia Management Panel, go to “Arrange G-SYNC,” after which click on the checkbox on the backside that claims “allow settings for the chosen show mannequin.”
This checkbox serves as a notification that the show shouldn’t be validated, however when enabled, it is going to perform successfully, significantly if it’s a more moderen product. The overwhelming majority of those newer displays have glorious adaptive sync implementations.
AMD FreeSync branding defined
AMD has additionally break up FreeSync into a number of courses: FreeSync, FreeSync Premium, and FreeSync Premium Professional. Let’s break down the variations…
AMD FreeSync
| AMD FreeSync |
| Helps Generic Adaptive Sync |
| AMD Licensed |
FreeSync is essentially the most fundamental tier of FreeSync displays, making certain solely that the monitor helps adaptive sync expertise. AMD certifies these merchandise to assist adaptive sync. Not each monitor that helps generic adaptive sync receives FreeSync branding, however a big quantity do.
Much like G-Sync, a monitor missing FreeSync branding can nonetheless assist adaptive sync and work properly on each AMD and Nvidia GPUs; it merely means the producer has opted to not model it as FreeSync. That is normal advertising and marketing observe.
AMD FreeSync Premium
| AMD FreeSync Premium |
| Extension of FreeSync Supporting Generic Adaptive Sync |
| Requires 120Hz at 1080p or Larger |
| Requires Low Framerate Compensation (LFC) Help |
FreeSync Premium extends FreeSync by requiring at the very least a 120Hz refresh price at a minimal decision of 1080p, and assist for low framerate compensation (LFC). LFC is a vital characteristic that extends variable refresh price assist under the monitor’s rated minimal refresh price by duplicating frames to a better refresh price. As an example, a monitor with a 48-144Hz refresh price vary may nonetheless function at 36 FPS with adaptive sync by LFC: the show would present every body twice and run at 72Hz.
Nvidia’s G-Sync branded displays (these with a G-Sync module) additionally use an equal of LFC, which Nvidia markets as supporting the “full variable refresh price vary” or “right down to 1Hz.” This has led to the misunderstanding that solely G-Sync displays assist full adaptive sync performance right down to 1Hz, however this isn’t true. Different adaptive sync displays (e.g., these with FreeSync branding) also can successfully work right down to 1Hz, offered they assist LFC. Basically all new gaming displays with refresh charges at or above 144Hz work on this means and assist LFC, however this was a extra important concern with earlier implementations 5 years in the past.
These days, gaming displays with excessive refresh charges sometimes obtain FreeSync Premium branding, whereas lower-tier or workplace displays get normal FreeSync branding. Even 60Hz shows can assist adaptive sync, often with a slim refresh price vary, however solely these above 120Hz qualify for FreeSync Premium.
AMD FreeSync Premium Professional
| AMD FreeSync Premium Professional |
| Extension of FreeSync Premium with Generic Adaptive Sync |
| HDR Help |
| Help for AMD FreeSync Premium Professional HDR Pipeline |
| Elevated AMD Certification & Validation |
FreeSync Premium Professional is used for displays that assist each adaptive sync and HDR capabilities. This contains compatibility with AMD’s particular HDR processing pipeline, in addition to what AMD describes as “meticulous shade and luminance certification.” Not like G-Sync Final, FreeSync Premium Professional doesn’t mandate a particular brightness stage; a monitor merely has to assist HDR and the FreeSync Premium Professional HDR pipeline to qualify.
How to make sure FreeSync is enabled
Similar to with non-G-Sync branded merchandise on Nvidia GPUs, displays with out FreeSync branding will perform correctly on AMD Radeon GPUs. However to verify adaptive sync is enabled in your monitor, head to Radeon Software program and beneath Gaming > Show, you must see a toggle to allow adaptive sync or FreeSync, relying in your monitor’s branding. More often than not, this setting is enabled by default, but it surely’s at all times value checking to make sure it is energetic.
Monitor high quality and certification (in observe)
Each AMD and Nvidia declare to certify and validate merchandise branded with their respective FreeSync and G-Sync labels, though this has by no means been a assure of superior efficiency. Now we have encountered loads of mediocre FreeSync merchandise and G-Sync merchandise, regardless of AMD’s declare that FreeSync Premium Professional displays have “meticulous shade certification” and Nvidia’s assertion that G-Sync Appropriate merchandise “don’t present artifacts.” These model names aren’t a top quality assurance.
In our expertise, merchandise branded as G-Sync and utilizing the G-Sync module usually tend to ship good efficiency than these in different tiers and branding. This is not a assure that G-Sync equates to good efficiency, and there are far fewer G-Sync merchandise than different branded merchandise. FreeSync and G-Sync Appropriate certification appears to be comparatively minimal, with a variety of shows qualifying for these manufacturers.
What we see in at present’s market is best understood when you think about that adaptive sync, FreeSync, and G-Sync had been established years in the past when variable refresh charges had been a growing expertise. Now that adaptive sync is extra mature and most show distributors have converged on {industry} requirements, FreeSync and G-Sync do not carry as a lot weight. AMD and Nvidia are largely utilizing these for advertising and marketing functions, moderately than to suggest one thing particular or distinctive.
Today, almost each new gaming show helps some type of adaptive sync, whether or not it is unbranded, FreeSync-branded, or G-Sync-branded. It is a ubiquitous characteristic, and we’d by no means suggest a gaming monitor with out it. There are some merchandise (a minority), the place adaptive sync is not supported in all modes or has flickering points, and we sometimes contemplate these as deal-breaking flaws that make a product exhausting to suggest.
By now, most gaming monitor producers have grasp on the best way to produce an adaptive sync monitor days and get it proper more often than not. As is at all times the case, it is not the stickers on the field or model names that make product, it is the efficiency, options, and value that truly matter.
Procuring Shortcuts:
- Alienware AW3423DW 34″ QD-OLED on Amazon
- Samsung Odyssey OLED G9 on Amazon
- Alienware AW3423DWF 34″ QD-OLED on Dell
- Samsung Odyssey OLED G8 on Amazon
- AMD Radeon RX 7900 XTX on Amazon
- AMD Radeon RX 7800 XT on Amazon
- Nvidia GeForce RTX 4070 Ti on Amazon
- AMD Radeon RX 7900 XT on Amazon
- Nvidia GeForce RTX 4090 on Amazon
[ad_2]
Source