Underground reservoir on Mars might fill oceans on the planet’s floor, examine finds

Join CNN’s Marvel Idea science publication. Explore the universe with news on fascinating discoveries, scientific advancements and more.
Information from a retired NASA mission has revealed proof of an underground reservoir of water deep beneath the floor of Mars, in keeping with new analysis.
A staff of scientists estimates that there could also be sufficient water, trapped in tiny cracks and pores of rock in the course of the Martian crust, to fill oceans on the planet’s floor. The groundwater would probably cowl the whole thing of Mars to a depth of 1 mile (1.6 kilometers), the examine discovered.
The info got here from NASA’s InSight lander, which used a seismometer to review the inside of Mars from 2018 to 2022.
Future astronauts exploring Mars would encounter a complete host of challenges in the event that they tried to entry the water, as a result of it’s situated between 7 and 12 miles (11.5 and 20 kilometers) beneath the floor, in keeping with the examine revealed Monday within the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
However the discovering uncovers new particulars concerning the geological historical past of Mars — and suggests a brand new place to seek for life on the pink planet if the water might ever be accessed.

“Understanding the Martian water cycle is important for understanding the evolution of the local weather, floor and inside,” mentioned lead examine creator Vashan Wright, assistant professor and geophysicist on the College of California, San Diego’s Scripps Establishment of Oceanography, in a press release. “A helpful place to begin is to determine the place water is and the way a lot is there.”
The seek for ‘misplaced’ water on Mars
Mars was probably a hotter, wetter place billions of years in the past, primarily based on the proof of historical lakes, river channels, deltas and rocks altered by water studied by different NASA missions and noticed by orbiters. However the pink planet misplaced its ambiance greater than 3 billion years in the past, which successfully ended the moist interval on Mars.
Scientists nonetheless aren’t certain why Mars misplaced its ambiance, and a mess of missions have been developed to be taught concerning the historical past of the planet’s water, the place it went, and whether or not water ever created liveable circumstances for all times on Mars. Whereas water stays trapped as ice on the planet’s polar ice caps, researchers don’t consider that may account for all of the planet’s “misplaced” water.
Current theories supply a number of probably eventualities for what occurred to Martian water after Mars misplaced its ambiance: Some hypothesize it grew to become ice or was misplaced to house, whereas others recommend it was included into minerals beneath the planet’s floor or trickled into deep aquifers.
The brand new findings recommend that water on Mars filtered down into the Martian crust.
InSight, brief for Inside Exploration utilizing Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Warmth Transport, was a stationary lander. Nevertheless it collected unprecedented knowledge concerning the thickness of the pink planet’s crust and the temperature of its mantle, in addition to the depth and composition of the core and ambiance. The lander’s seismometer detected the primary quakes on one other planet, dubbed marsquakes.
Whereas earthquakes happen when tectonic plates shift, transfer and grind in opposition to each other, the Martian crust is like one big plate with faults and fractures because the planet continues to shrink and funky over time. Because the Martian crust stretches, it cracks, and InSight’s seismometer was in a position to detect greater than 1,300 marsquakes as they rumbled from a whole lot and hundreds of miles away.
Scientists finding out InSight’s knowledge have been in a position to examine the pace of marsquakes as they traveled by the planet, which may function an indicator of what substances exist beneath the Martian floor.
The pace of seismic waves is dependent upon what the rock is product of, the place it has cracks and what fills these cracks, Wright mentioned.
The staff used this knowledge and fed it right into a mathematical mannequin of rock physics, which is used on Earth to map underground oil fields and aquifers.
The outcomes confirmed that InSight’s knowledge finest matches up with a deep layer of igneous, or volcanic, rock that’s crammed with liquid water.

“Establishing that there’s a large reservoir of liquid water offers some window into what the local weather was like or may very well be like,” mentioned examine coauthor Michael Manga, a professor of earth and planetary science on the College of California, Berkeley, in a press release.
“And water is critical for all times as we all know it. I don’t see why (the underground reservoir) isn’t a liveable surroundings,” Manga added. “It’s actually true on Earth — deep, deep mines host life, the underside of the ocean hosts life. We haven’t discovered any proof for all times on Mars, however at the very least we’ve recognized a spot that ought to, in precept, be capable of maintain life.”
If Mars’ crust is analogous throughout the planet, there could also be extra water inside the mid-crust zone than the “volumes proposed to have crammed hypothesized historical Martian oceans,” the authors wrote within the examine.
Rocks assist entice details about the historical past of a planet, and understanding the water cycle of a planet might help researchers unlock the evolution of Mars, Wright mentioned.
Whereas the evaluation of the info can’t reveal any details about life, previous or current, if it existed on Mars, it’s attainable that moist Martian crust may very well be liveable in the identical means that deep groundwater on Earth is hospitable for microbial life, he mentioned.
However even drilling holes simply half a mile (1 kilometer) or deeper on Earth is a problem that requires vitality and infrastructure, so an enormous variety of assets would have to be delivered to Mars to drill to such depths, Wright mentioned.
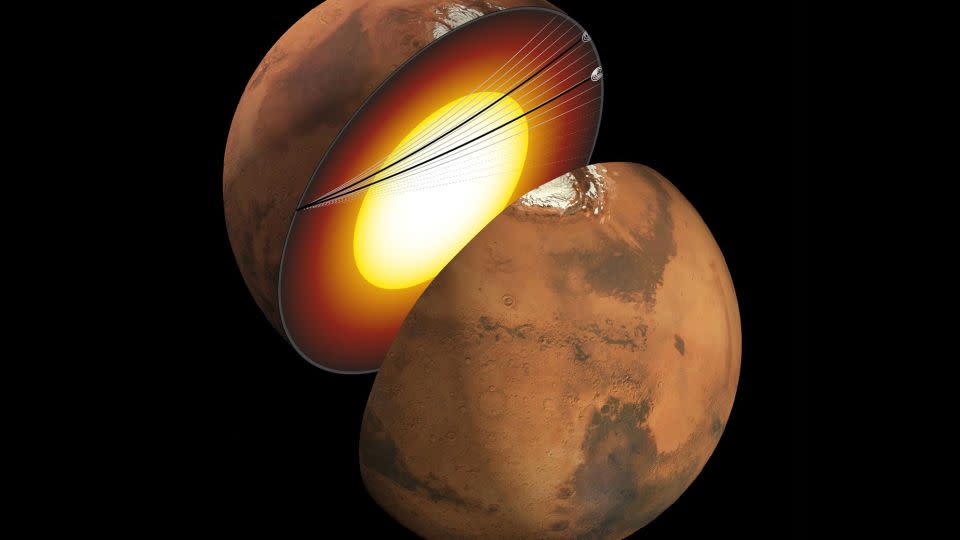
The staff was shocked to not discover proof suggesting a layer of frozen groundwater beneath Perception as a result of that portion of the crust is chilly. The researchers are nonetheless attempting to find out why there isn’t frozen groundwater at shallower depths above the mid-crust.
Home windows into Martian historical past
The findings add a brand new piece to the Martian water puzzle.
The concept liquid water might exist deep beneath the Martian floor has been round for many years, however that is the primary time actual knowledge from a Mars mission can verify such hypothesis, mentioned Alberto Fairén, a visiting interdisciplinary planetary scientist and astrobiologist inside the division of astronomy at Cornell College. Fairén was not concerned within the examine.
He mentioned the water is probably going “a form of deep underground mud.”
“These new outcomes display that liquid water does exist within the Martian subsurface at present, not within the type of discrete and remoted lakes, however as liquid water-saturated sediments, or aquifers,” Fairén mentioned. “On Earth, the subsurface biosphere is actually huge, containing many of the prokaryotic variety and biomass on our planet. Some investigations even level to an origin of life on Earth exactly deep within the subsurface. Subsequently, the astrobiological implications of lastly confirming the existence of liquid water habitats kilometers beneath the floor of Mars are actually thrilling.”

The result’s “precisely the form of factor that I hoped we might get out of InSight,” mentioned Bruce Banerdt, the principal investigator for the InSight mission.
“I hoped that we might get knowledge that was adequate to do these sorts of research the place we’re really taking a look at particulars of the within of Mars which are related to geological questions, questions concerning the habitability of Mars, questions concerning the evolution of Mars,” he mentioned.
Banerdt, who was not concerned within the analysis, mentioned that whereas the interpretation of the info introduced within the paper is strongly supported with good arguments, he additionally believes it’s nonetheless considerably speculative and that there’s nearly at all times one other solution to clarify any given set of knowledge.
“I used to be actually impressed by the truth that Wright et al introduced in mineral physics ideas to interpret seismic knowledge,” Banerdt mentioned.
Banerdt and Wright each expressed an curiosity within the capability to ship extra seismometers to Mars and different planets and moons inside our photo voltaic system sooner or later. Whereas InSight’s one seismometer gathered essential knowledge, spreading them out throughout Mars would reveal variations inside the planet’s inside and supply a larger window into its numerous and complicated historical past, Banerdt mentioned.
“Simply as on Earth, the place groundwater is linked to the floor by rivers and lakes, this was certainly the case on early Mars as nicely,” Wright mentioned. “The groundwater we see is a report of that previous.”
For extra CNN information and newsletters create an account at CNN.com




