Webb telescope friends into our galaxy’s outskirts, sees gorgeous scene

The far outskirts of our galaxy are teeming with exercise.
Astronomers pointed the highly effective James Webb Space Telescope at a distant zone dubbed the “Excessive Outer Galaxy,” and zoomed in on dense cosmic clouds containing clusters of stars. In unprecedented decision of this area, they noticed vibrant star formation, and potent jets of fabric ejecting from these sizzling objects.
“What was fascinating and astounding to me from the Webb information is that there are a number of jets capturing out in all totally different instructions from this cluster of stars,” NASA scientist Mike Ressler, who led observations, stated in a statement. “It’s just a little bit like a firecracker, the place you see issues capturing this fashion and that.”
SEE ALSO: NASA scientist viewed first Voyager images. What he saw gave him chills.
You possibly can see this exercise beneath in a area of Digel Cloud 2S. Amid this cluster of younger stars are jets zipping out from the cluster. Younger stars emit these jets of fuel and mud from their poles, which journey into space.
“It’s just a little bit like a firecracker, the place you see issues capturing this fashion and that.”
And there is added cosmic eye sweet. Past these dynamic stars on the fringe of the Milky Way galaxy, you possibly can spot a variety of distant galaxies, proven in reddish and greenish colours. Many of those are spiral galaxies, like ours.
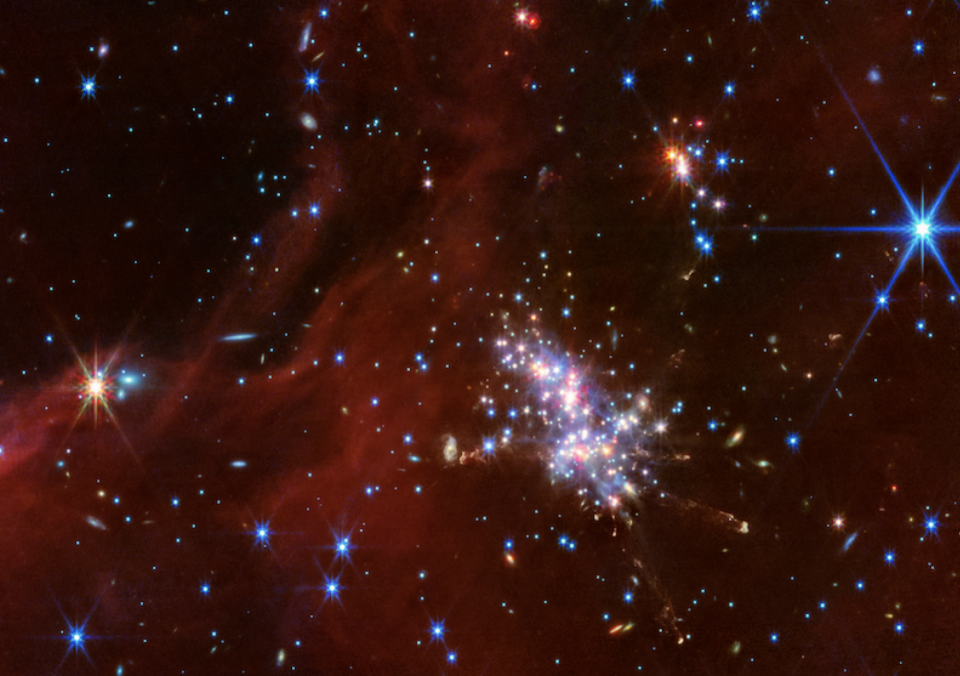

A vibrant star-forming area within the “Excessive Outer Galaxy,” as captured by the James Webb Area Telescope. Credit score: NASA / ESA / CSA / STScI / M. Ressler (JPL)
The “Excessive Outer Galaxy” is situated over 58,000 light-years (a light-year is sort of 6 trillion miles) from the middle of our galaxy. Earth, in the meantime, is a few 26,000 light-years from the middle.
This newest Webb analysis, revealed within the peer-reviewed Astronomical Journal, gives novel observations in scientists’ quest to completely grasp how stars kind in several galactic environments.
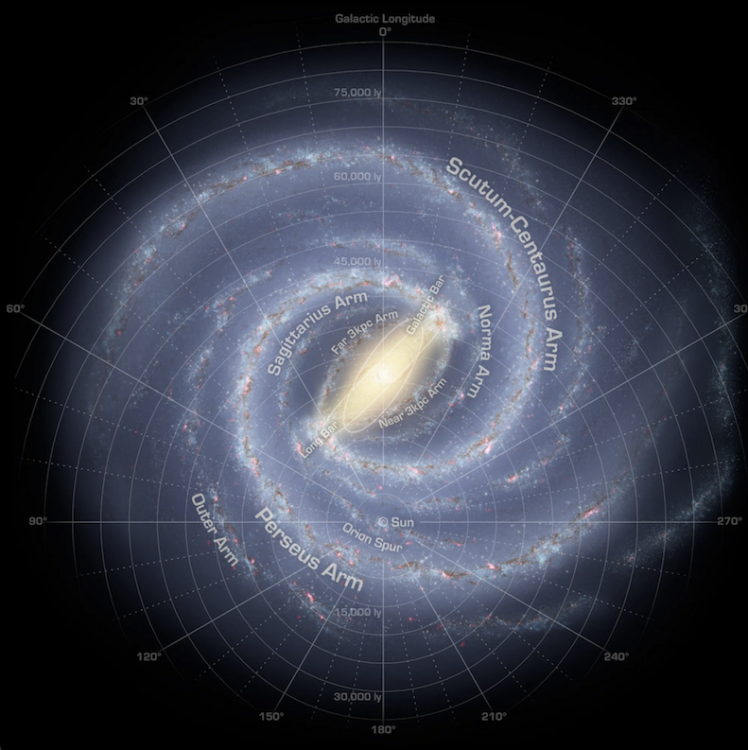
A graphic of the Milky Manner galaxy, with the solar proven beneath the galactic heart. Credit score: NASA / JPL-Caltech / R. Harm (SSC / Caltech)
The Webb telescope’s highly effective skills
The Webb telescope — a scientific collaboration between NASA, ESA, and the Canadian Area Company — is designed to look into the deepest cosmos and reveal new insights in regards to the early universe. However it’s additionally inspecting intriguing planets in our galaxy, together with the planets and moons in our solar system.
This is how Webb is reaching unparalleled feats, and likely will for decades to come:
– Large mirror: Webb’s mirror, which captures gentle, is over 21 toes throughout. That is over two-and-a-half instances bigger than the Hubble Space Telescope’s mirror. Capturing extra gentle permits Webb to see extra distant, historic objects. The telescope is peering at stars and galaxies that fashioned over 13 billion years in the past, just some hundred million years after the Large Bang. “We’ll see the very first stars and galaxies that ever fashioned,” Jean Creighton, an astronomer and the director of the Manfred Olson Planetarium on the College of Wisconsin–Milwaukee, instructed Mashable in 2021.
– Infrared view: Not like Hubble, which largely views gentle that is seen to us, Webb is primarily an infrared telescope, which means it views gentle within the infrared spectrum. This permits us to see way more of the universe. Infrared has longer wavelengths than seen gentle, so the sunshine waves extra effectively slip via cosmic clouds; the sunshine does not as typically collide with and get scattered by these densely packed particles. In the end, Webb’s infrared eyesight can penetrate locations Hubble cannot.
“It lifts the veil,” stated Creighton.
– Peering into distant exoplanets: The Webb telescope carries specialized equipment called spectrographs that can revolutionize our understanding of those far-off worlds. The devices can decipher what molecules (resembling water, carbon dioxide, and methane) exist within the atmospheres of distant exoplanets — be they fuel giants or smaller rocky worlds. Webb appears at exoplanets within the Milky Manner galaxy. Who is aware of what we’ll discover?
“We’d study issues we by no means considered,” Mercedes López-Morales, an exoplanet researcher and astrophysicist on the Center for Astrophysics-Harvard & Smithsonian, instructed Mashable in 2021.
Already, astronomers have efficiently discovered intriguing chemical reactions on a planet 700 light-years away, and have began one of the vital anticipated locations within the cosmos: the rocky, Earth-sized planets of the TRAPPIST solar system.




