James Webb telescope watches historic supernova replay 3 instances — and confirms one thing is critically mistaken in our understanding of the universe
[ad_1]
If you purchase via hyperlinks on our articles, Future and its syndication companions could earn a fee.

The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) has found yet one more troubling signal that there is one thing very mistaken with our mannequin of the universe.
Relying on which a part of the universe astronomers measure, the cosmos appears to be rising at completely different charges — an issue scientists name the Hubble pressure. Measurements taken from the distant, early universe present that the enlargement charge, known as the Hubble fixed, intently matches our greatest present mannequin of the universe, while those taken nearer to Earth threaten to break it.
Now, a brand new research utilizing the gravitationally-warped gentle of a ten.2 billion light-year distant supernova has revealed that the thriller could possibly be right here to remain. The researchers launched their findings in a series of papers in The Astrophysical Journal. The Hubble pressure calculations have additionally been accepted for publication within the journal, and are posted in a paper on the pre-print database arXiv.
“Our workforce’s outcomes are impactful: The Hubble fixed worth matches different measurements within the native universe, and is considerably in pressure with values obtained when the universe was younger,” co-author Brenda Frye, an affiliate professor of astronomy on the College of Arizona said in a statement.
Associated: ‘It could be profound’: How astronomer Wendy Freedman is trying to fix the universe
At the moment, there are two gold-standard strategies for determining the Hubble fixed. The primary entails poring over tiny fluctuations within the cosmic microwave background, an historic relic of the universe’s first gentle produced simply 380,000 years after the Big Bang. This technique enabled astronomers to deduce an enlargement charge of roughly 67 kilometers per second per megaparsec (km/s/Mpc), which intently matches predictions made by the standard model of cosmology.
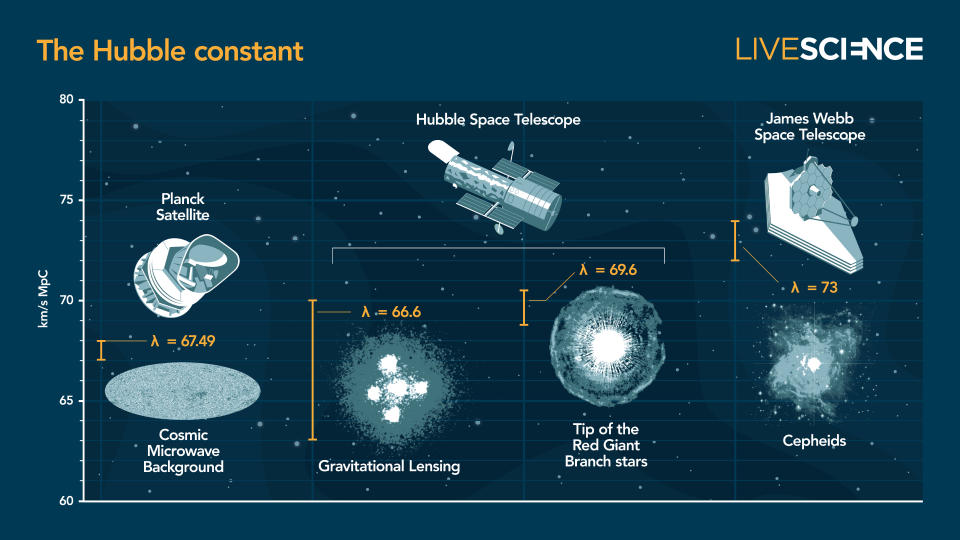
However the second technique, measuring nearer distances with pulsating stars known as Cepheid variables, contradicts this — returning a puzzlingly excessive worth of 73.2 km/s/Mpc. This discrepancy superficially could not look like a lot, however it’s sufficient to fully contradict the predictions made by the usual mannequin. In line with the mannequin, a mysterious entity often called darkish vitality is meant to be driving the universe’s expansion at a constant rate, however the brand new findings throw a wrench on this understanding.
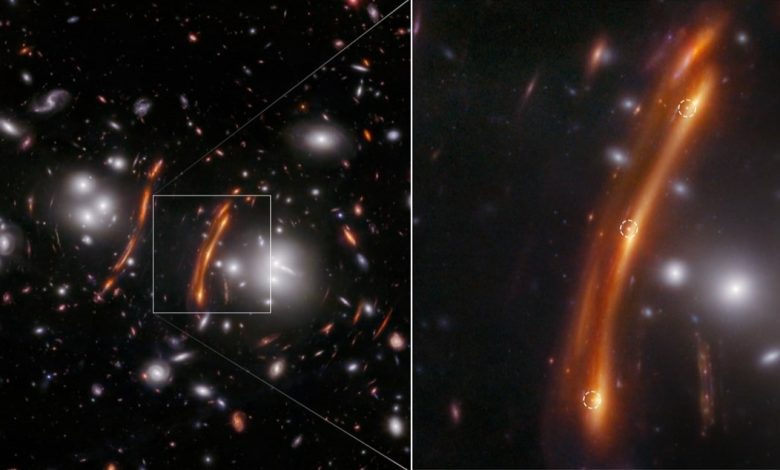
Within the new research, astronomers pointed JWST’s near-infrared digital camera (NIRCam) on the galaxy cluster PLCK G165.7+67.0, also referred to as G16, which is situated 3.6 billion light-years from Earth. There, they noticed three distinct factors of sunshine that got here from a single sort IA supernova whose gentle had been each magnified and bent, or gravitationally lensed, by a galaxy in entrance of it.
Kind Ia supernovae happen when the fabric from one star falls onto the embering husk of a useless star, often called a white dwarf, resulting in a big thermonuclear explosion. These explosions are thought to all the time occur on the identical brightness, making them “commonplace candles” from which astronomers can measure far-off distances and calculate the Hubble fixed.

RELATED STORIES
—After 2 years in space, the James Webb telescope has broken cosmology. Can it be fixed?
—James Webb telescope discovers oldest black hole in the universe
—8 stunning James Webb Space Telescope discoveries made in 2023
Comply with-up observations made with the ground-based A number of Mirror Telescope and Giant Binocular Telescope, each in Arizona, confirmed the dots’ level of origin.
By learning the time delays between the dots and plugging them, alongside the supernova’s distance, into varied fashions of gravitational lensing, the researchers produced a Hubble fixed worth of 75.4 km/s/Mpc, plus 8.1 or minus 5.5 — flatly contradicting the usual mannequin as soon as extra.
The calculation is unlikely to be the ultimate phrase on the strain, with different research groups pursuing their very own traces of investigation into the cosmic conundrum. For his or her half, the researchers behind the brand new research say that they may proceed to collect very important clues from different exploding stars discovered across the galaxy.
[ad_2]
Source